A spatial [3x3] fixed axis rotation matrix defined by three Euler angles in the x-convention (Z-X-Z).
Namespace:
ceometric.VectorGeometryAssembly: ceometric.VectorGeometry (in ceometric.VectorGeometry.dll) Version: 1.8.0.0 (1.8.0.0)
 Syntax
Syntax
| C# |
|---|
public static Matrix3d RotationEuler( double phi, double theta, double psi ) |
| Visual Basic (Declaration) |
|---|
Public Shared Function RotationEuler ( _ phi As Double, _ theta As Double, _ psi As Double _ ) As Matrix3d |
| Visual C++ |
|---|
public: static Matrix3d^ RotationEuler( double phi, double theta, double psi ) |
Parameters
- phi
- Type: System..::.Double
The angle in [radian] of the first rotation. Rotates counterclockwise around the global Z-axis.
- theta
- Type: System..::.Double
The angle in [radian] of the second rotation. Rotates counterclockwise around the global X-axis.
- psi
- Type: System..::.Double
The angle in [radian] of the third rotation. Rotates counterclockwise around the global Z-axis (again).
Return Value
Returns a [3x3] rotation matrix defined by three Euler angles in the x-convention (Z-X-Z). Remarks
Remarks
The z-x-z convention is the most common Euler rotation convention.
"global axis" means that the axis of rotation is fixed during the rotation.
See RotationTaitBryan(Double, Double, Double) for moving axis rotation.
 Examples
Examples
The following example illustrates the rotation convention:
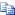 CopyC#
The coordinates of the rotated point are rotatedPoint = (0,0,1). This can be split into the following partial rotations:
CopyC#
The coordinates of the rotated point are rotatedPoint = (0,0,1). This can be split into the following partial rotations:
Point p = new Point(1,0,0); Matrix3d rMat = Matrix3d.RotationEuler(Math.PI/2, Math.PI/2, Math.PI/2); Point rotatedPoint = rMat * p;
- rotate p = (1,0,0) with phi = 90 degrees around the global z-Axis: p1 = (0,1,0)
- rotate p1 = (0,1,0) with theta = 90 degrees around the global x-Axis: p2 = (0,0,1)
- rotate p2 = (0,0,1) with psi = 90 degrees around the global z-Axis (again): p3 = (0,0,1)